Ecological Succession

Ecological succession is the gradual process by which ecosystems change and develop over time. Nothing remains the same and habitats are constantly changing. In order to understand succession, it is necessary to clearly understand the difference between these four terms:
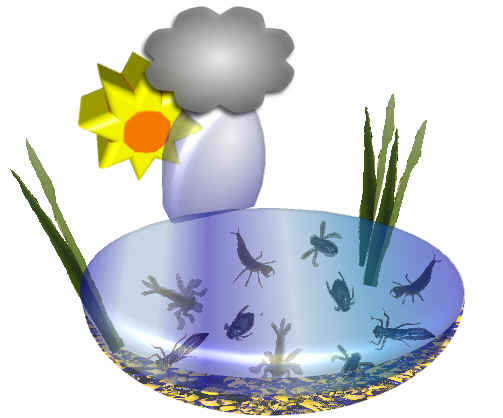
A place where organisms live e.g. a pond.
Pond
A group of individuals of the same species in a particular location.
For example, all of the Great Diving Beetle larvae and adults in the pond. See Great Diving Beetles up close.
All of the populations of species in a given area.
For example, all of the numerous species of micro-organisms, plants and animals living in the pond.
The community, together with
the physical and chemical
The pond ecosystem includes all of the non-living components - the water, the soil surrounding the pond, the mud on the bottom, the weather and microclimate, together with the living community of organisms.
Continue to |