| Basidiomycetes | Ascomycetes |
|||
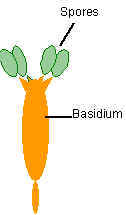
Fungi with spores produced externally, on specialised cells called basidia. Typically, there are 4 spores per basidium, although this varies from 1 to many, depending on the species. |
 |
|
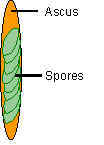
Fungi with spores produced inside a sac called an
ascus. Each ascus usually contains 8 spores (sometimes 4, depending on the species). |
|